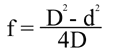Determining Focal Length of a
Lens--Bessel Method
[ HomePage | Experiments
| Equipment | Data
Analysis | Software | Techniques
]
Overview:
Suppose an object and screen are a fixed distance D apart. A
converging lens located between the object and screen will form a
real image on the screen at two distances whose separation is d and
is given by:
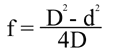
Note that the above relationship is derived in the note
[note4.pdf] which
gives examples of using matrices in geometric optics.
Goal of this Experiment: The
goal of this experiment is to determine the focal length of a lens by
locating the two positions where a real image of the object is formed
on the screen. A schematic of the lab set-up is shown below.
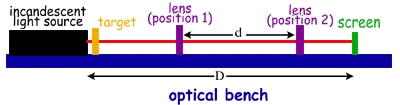
Suggested Procedures:
- Set up the apparatus as shown above. The crossed arrow target
will be used as the "object," and its image will be projected onto
the screen. The object to screen distance must be greater than
four times the focal length of the lens being used. Record the
distance between the target and the screen.
- Determine the two positions of the converging lens which yield
a clear image of the target on the screen.
- Repeat the procedure with various target to screen
distances.
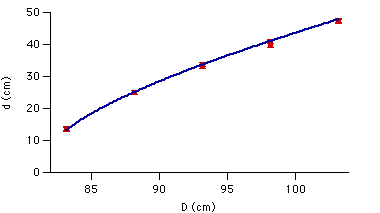
Sample Data:
The plot below shows data taken with this set-up of the
experiment. The data displayed here were fit to a function of the
form:
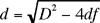
Questions:
- What is your estimate of the random and systematic errors in
determining d and D ?
- What is the resulting error on your determination of the focal
length ?